Enum
Enumeration types are given as
EnumType = enum EnumTable
This means the EnumType is enum type. Constants are stored in EnumTable table. It doesn't matter what is the real type of the EnumType. Mission developer must NEVER operate constant values! Only constant names must be used!
Array
Given as
ArrayType = array of ElementType
This means ArrayType is table that contains ElementType
ArrayType = {
[1] = ElementType,
[2] = ElementType,
...
[N] = ElementType
}
Map
Given as
MapType = map KeyType, ElementType
This means MapType is table that contains ElementType each with key of type KeyType.
MapType = {
[KeyType] = ElementType,
[KeyType] = ElementType,
...
[KeyType] = ElementType
}
Time
Time = number
Time is given in seconds.
Model time is the time that drives the simulation. Model time may be stopped, accelerated and decelerated relative real time.
Mission time is a model time plus time of the mission start.
Distance
Distance = number
Distance is given in meters.
Angle
Angle = number
Angle is given in radians.
Azimuth = Angle
Azimuth is an angle of rotation around world axis y counter-clockwise.
Mass
Mass = number
Mass is given in kilograms.
Coordinate system
DCS world has 3-dimensional coordinate system. DCS ground is an infinite plain.
Main axes:
Vectors
Vec3 type is a 3D-vector. It is a table that has following format:
Vec3 = {
x = Distance,
y = Distance,
z = Distance
}
Vec2 is a 2D-vector for the ground plane as a reference plane.
Vec2 = {
x = Distance,
y = Distance
}
Vec2.x = Vec3.x Vec2.y = Vec3.z
Another coordinate systems
Geographic coordinates are represented by latitude/longitude pair given in degrees.
GeoCoord = number
Latitude positive direction is North. Longitude positive direction is East.
MGRS coordinates are represented by table:
MGRS = {
UTMZone = string,
MGRSDigraph = string,
Easting = number,
Northing = number
}
MGRS.UTMZone identifies MGRS zone.
MGRS.MGRSDigraph is a pair of letters - identifier of 100x100 km square in the zone.
MGRS.Easting/MGRS.Northing pair determines location within the 100x100 km square. Precision depends on how many digits used. no digits - precision level 100 km 1 digits - precision level 10 km 2 digits - precision level 1 km 3 digits - precision level 100 m 4 digits - precision level 10 m
Orientation
Object orientation is represented by 3x3 orthogonal row-major matrix. Matrix rows are orthogonal normalized vectors (also called unit vectors):
Orientation = {
x = Vec3,
y = Vec3,
z = Vec3
}
A "normalized vector", also known as a "unit vector", is a vector that has a length equal to 1.
As an example, an object that was oriented pointing due east, with its top pointed straight up, would have the following set of orientation vectors:
Orientation = {
x = { x = 0, y = 0, z = 1},
y = { x = 0, y = 1, z = 0},
z = { x = -1, y = 0, z = 0}
}
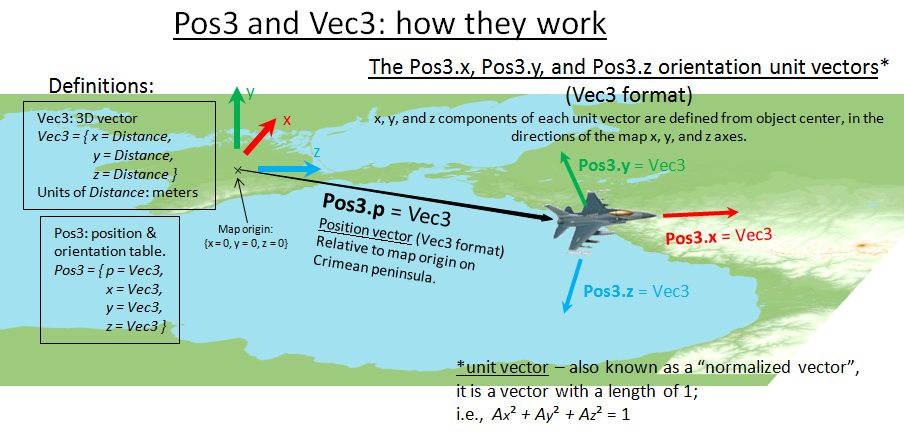
Position
Position is a composite structure. It consists of both coordinate vector and orientation matrix.
Position3 (also known as "Pos3" for short) is a table that has following format:
Position3 = { p = Vec3,
x = Vec3,
y = Vec3,
z = Vec3 }
An illustration of the Pos3 structure and how it relates to simulation objects is shown below.
Box3
Box3 = {
min = Vec3,
max = Vec3
}
3-dimensional box.
TypeName
TypeName = string
Each object belongs to a type. Object type is a named couple of properties those independent of mission and common for all units of the same type. Name of unit type is a string. Samples of unit type: "Su-27", "KAMAZ" and "M2 Bradley".
AttributeName
AttributeName = string
Each object type may have attributes.
Attributes are enlisted in ./Scripts/Database/db_attributes.Lua.
To know what attributes the object type has, look for the unit type script in sub-directories planes/, helicopter/s, vehicles, navy/ of ./Scripts/Database/ directory.
Desc
Desc = {
typeName = TypeName, --type name
displayName = string, --localized display name
attributes = array of AttributeName --object type attributes
}
Each object type has its own descriptor. Descriptor is a table that contains common information about all objects of this type, including common and specific (depending on object category and type) parameters. All descriptors inherit Desc.








