DCS: Black Shark 2 is a simulation of the Russian Ka-50 attack helicopter and the next entry in the Digital Combat Simulator combat series. DCS: Black Shark 2 is a greatly improved version of the original DCS: Black Shark that brings many new features.
The Ka-50 "Black Shark" is a unique and deadly single-seat, Russian attack helicopter that has seen combat in the Northern Caucasus. It combines a high performance dual rotor system with a deadly weapons payload of guided missiles, rockets, bombs, and a 30mm cannon. The Ka-50 is also unique in that it has an ejection seat.
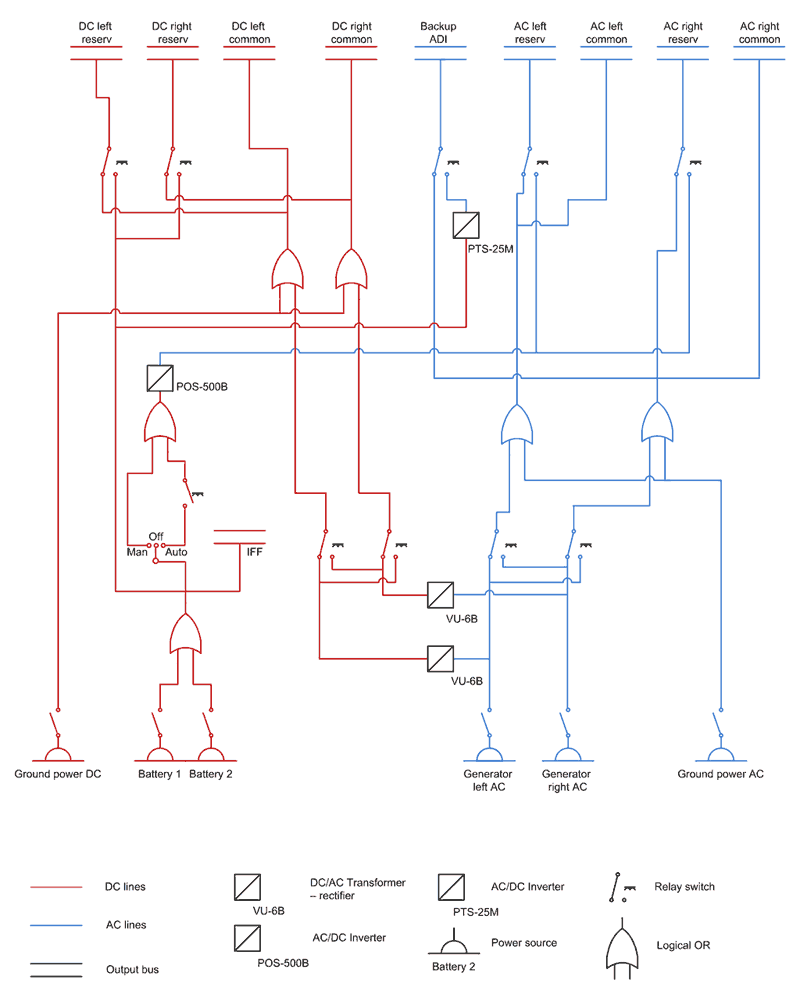
The electrical system includes:
The Ka-50 electrical power generation system provides AC and DC power to the primary and emergency buses and distribution assemblies. This power supply is used to run avionics systems, internal and external lighting, hydraulic, fuel systems control and monitoring, engines, and auxiliary power unit start up systems. When on the ground, an external power cart can be used as an alternate power source. In addition to onboard power generation capability, the Ka-50 also includes batteries that electrical power can be drawn from.
The Alternating Current System
The primary electrical system is fed by alternating current (AC) 115/200 V, 400 Hz generators. This supply is further divided into left and right systems on independent channels to provide system redundancy. Generator operation is dependent upon the left and right engines being active as each engine contains a gearbox that runs a generator. The left channel systems can be powered by the right generator and the right channel systems are powered by the left generator. In the event of both generators becoming inoperative, a back-up, static DC to AC inverter can take over power to the most important systems and direct current will trigger the in-flight warning system.
The Direct Current System
Systems requiring direct current (DC) power are supplied at 27V by use of AC to DC transformer-rectifiers. Transformer-rectifiers are active while the generators are in operation. If one of the transformer-rectifiers is switched off though, systems will be switched to the operating transformer-rectifier. If both transformer-rectifiers and/or generators are off-line, the most important avionics systems will be switched to emergency DC power.
Damage to the electrical generation system is also manifested in the visual damage model of the Ka-50. An event-oriented approach is implemented such that a loss in electrical power to systems will have a cascade effect. This specifically means that the loss of one electrical system will have repercussions affecting linked elements of the electrical system.
Although a highly detailed flight manual will be provided with DCS: Black Shark, the following provides you with a small sampling of the avionics systems modeled in our simulation of the Ka-50. Piloting, navigation, targeting and defensive systems and included in this overview.

The Ka-50 cockpit instruments are generally traditional electro-mechanical gauges that are mounted on the front dash and side / back panels. These instruments are divided into three general groups: flight control, engine control/monitoring and systems control. Other cockpit interfaces include traditional switches, dials and multiple-position switches. Additionally, the Ka-50 has multiple banks of warnings lights and cockpit illumination controls.
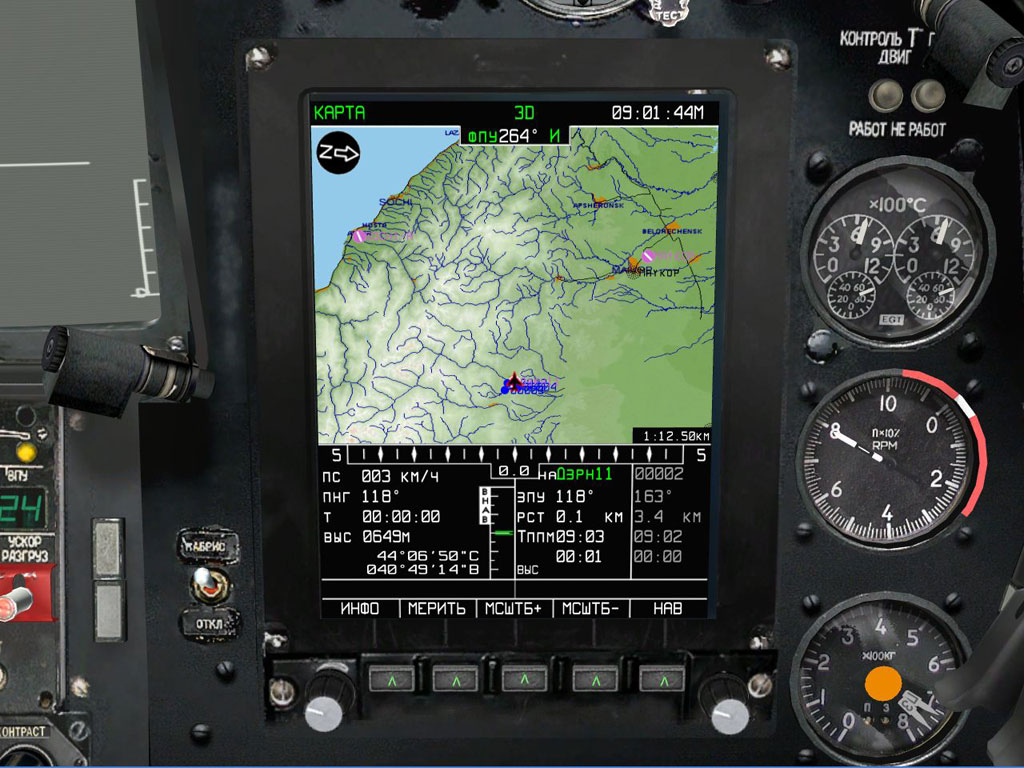
The ABRIS panel is a multi-function display that allows the pilot to perform the following tasks:

The targeting-navigation system is designed to integrate combat, navigation and flight tasks by processing both digital and analog information. «Rubicon» is integrated with the «Shkval» targeting system, airborne information display system and weapon control system.
«Radian» is a sub-system of «Rubicon» that helps automate flight navigation. «Radian» can store information in its memory such as coordinates for two airfields, six waypoints of a flight plan, ten operative targets, and four reference points.
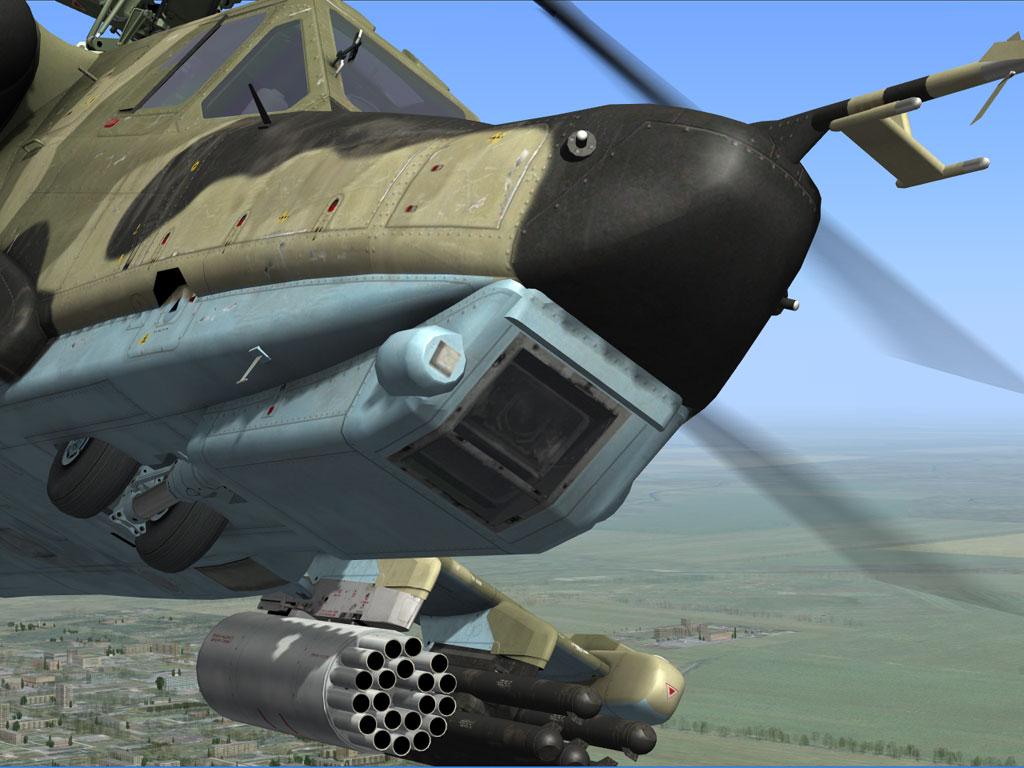


The «Shkval» system consists of a television camera combined with a laser range-finder and laser illumination designator to guide the anti-tank missile system.
The «Shkval» system can be ground-stabilizing and is capable of auto-tracking a designated target. There are two Fields Of View (FOV) levels: Wide FOV with a 6x magnification and narrow FOV with a 22x magnification. FOV gimbal suspension limits are: ±35° in azimuth and +15° to -80° in elevation.
The video picture is shown as a gray-scale image on the IT-23VM TV monitor.
The «Shkval» can be set to scan for targets automatically and the angular rate of scan can be manually be set by the pilot while in the cockpit.
To slew the «Shkval» camera, the pilot uses a small mini-stick on the helicopter cyclic.








