El P-51D Mustang no es sólo uno de los aviones más emblemáticos jamás construidos, sino también posiblemente el cazabombardero polivalente más eficaz de la Segunda Guerra Mundial. Armado con seis ametralladoras Browning del calibre 50, el Mustang también podía transportar dos bombas o hasta diez cohetes no guiados.
El Mustang comenzó sus operaciones de combate en la RAF en abril de 1942, demostrando inmediatamente su eficacia como caza y en los ataques de caza-bombardero a baja altura "Rhubarb" contra aeródromos enemigos, trenes de suministros y en la función de apoyo aéreo cercano. Dominaba especialmente los combates aéreos por encima de los 20.000 metros. Con sus elegantes líneas, su característica cabina de burbuja y sus alas recortadas, la versión "D" se convirtió rápidamente en el pilar de la 8ª Fuerza Aérea de los Estados Unidos en Europa.
Propulsado por el Packard V-1650-7, una versión del Rolls-Royce Merlin 66 fabricada bajo licencia con sobrealimentador de dos etapas y dos velocidades, el Mustang tenía una velocidad máxima de 390 millas por hora y una autonomía de combate de aproximadamente 750 millas (1.200 km). El uso de tanques de combustible externos aumentó el alcance operativo del P-51D a 2.200 km, permitiéndo escoltar a los bombarderos aliados en misiones de largo alcance hasta el corazón de Alemania. El P-51D desempeñó un papel fundamental en el establecimiento de la superioridad aérea aliada durante la invasión de Normandía el Día D de junio de 1944, y en el mantenimiento de la supremacía aérea mientras las fuerzas aliadas se abrían paso hacia Berlín.
Los pilotos del Mustang consiguieron casi 5.000 victorias sobre aviones enemigos en la Segunda Guerra Mundial. El DCS: P-51D es un módulo magnífico. Vuélalo y compruébalo por ti mismo.
The North American Aviation P-51D fighter aircraft is a single-seat, low wing monoplane powered by a 12 cylinder V-1650-7 liquid cooled, Packard built Rolls Royce "Merlin" engine. The engine is equipped with a two-speed, two-stage supercharger and an automatic manifold pressure regulator. The engine spins a four blade Hamilton Standard Hydromatic constant speed propeller.
The Packard engine delivers approximately 1,490 horse power at sea level. The maximum altitude is approximately 40,000 feet. The supercharger ratios are approximately 6 to 1 in low blower mode and 8 to 1 in high blower mode.
The fuselage is a semi-monocoque, all-metal structure. The all-metal wings are built in two halves which are joined at the aircraft center line and are of full cantilever structure. The airfoil is of laminar-flow design, which provides low drag even at high speed. The tail section is metal with fabric-covered elevator and rudder control surfaces. The aircraft is flush-riveted throughout – another factor contributing to its great speed.
Two fuel tanks with a total capacity of 184 U.S. gallons are located inside the wing and an additional 85 gallon fuselage fuel tank is located aft of the cockpit.
The armament consists of six .50 caliber machine guns mounted in the wings. Streamlined bomb racks installed beneath each wing panel can accommodate one 100, 300, or 500-lb. bomb each, or a depth charge or chemical tank. The bomb racks can be easily removed. Bombs may be substituted by droppable combat fuel tanks with a capacity of 75 or 110 U.S. gallons each for long-range operations. The wing can also support up to 10 unguided rockets, or up to 6 if bombs are also loaded.
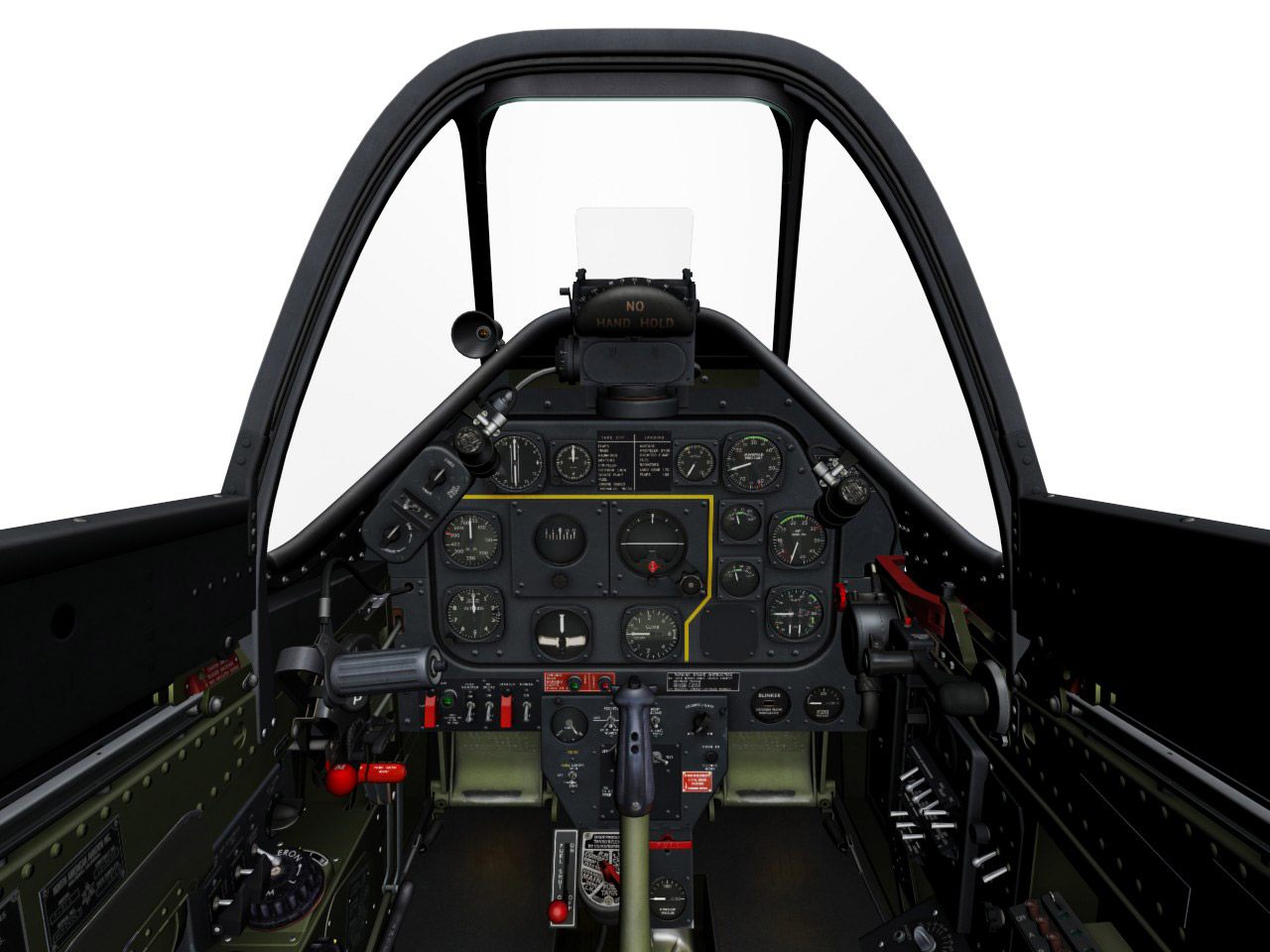
The DCS: P-51D cockpit is a 100% six-degrees of freedom (6 DOF) cockpit that allows complete freedom of movement around the cockpit. Each panel is reproduced in exacting detail to match 1940s era P-51Ds. This includes all panels, switches, dials, buttons being animated, rendered in the 3D, and with high-resolution textures. Both day and night lighting is available.
When the mouse is hovered over a cockpit control, a tool tip is displayed to indicate the controls function.

Multi-layer sample recordings from "Miss Velma" P-51D and controlled with physical model parameters provide the distinctive Mustang sound.
The P-51D model is a very precise and accurate of the Mustang that includes:
The power plant of the P-51D is a liquid-cooled, 12-cylinder Rolls-Royce Merlin V-1650-7, built in the U.S. by the Packard Motor Car Company. It is equipped with an injection-type carburetor, a two-speed, two-stage supercharger, and develops over 1400 hp on takeoff.
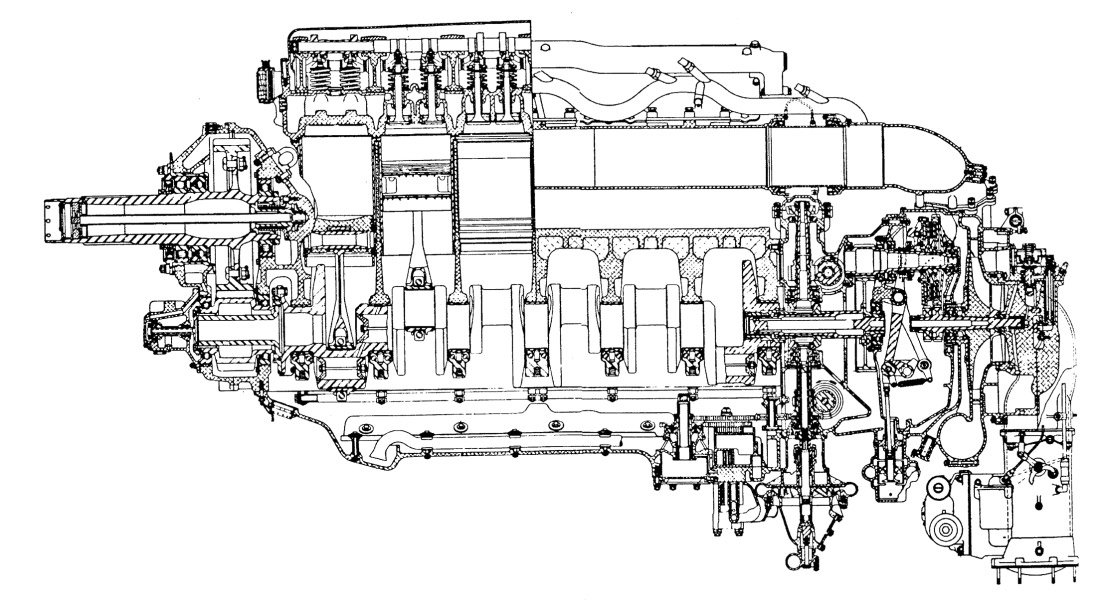
The supercharger installed on the Packard Merlin engine includes two compressor stages that deliver air from the carburetor intake to the pistons under much greater pressure than would be possible through direct aspiration, allowing a greater fuel-air mixture to be burned and increasing power output.
The carburetor provides automatic control of the fuel-air mixture passed from the air intake to the supercharger and onto the engine manifold for combustion in the cylinders.
In order to provide an extra boost to the engine in extreme situations, the throttle can be moved past the gate stop by the quadrant to break the safety wire. The engine will then be opened up to its absolute limit and will give approximately 6 in. of additional manifold pressure in excess of the normal full throttle setting of 61 in. (with mixture control set to RUN or AUTO RICH and prop set for 3000 RPM.) This throttle reserve is called War Emergency Power (WEP) and should be used only in extreme situations. If used for more than 5 minutes at a time, vital parts of the engine may be damaged.








