The Mil Mi-8MTV2 (NATO Hip E) is the armed version of the Russian-built, medium lift twin-turbine combat transport and utility helicopter. The Mi-8MTV2’s six external hard points enable it to carry a wide variety of weapons. These include up to 6 x 100 kg or 250 kg, or 2 x 500 kg bombs; 23 mm and 30 mm gun pods; and 80mm rocket pods (120 rockets - HE, AP, Frag, Illum). The Hip E can also mount 12.7mm (0.5 inch) heavy machine guns in a side pod and on a swivel door-pintle.
One of the most successful military helicopters ever built, the Mil Mi-8 entered Soviet Air Force service in 1967. Able to carry up to 24 fully-armed combat troops, the Mi-8T series was also adapted to fire unguided-rockets. More than 17,000 Mil Mi-8 variants have been built, and it is in use with 50 countries.
The Hip E has a cruising speed of approximately 230 kph, a combat radius of 600 km and can carry loads of up to 6000 kg. It has seen combat all over the world, most extensively in the 1979-1989 Russian-Afghan War, where it proved to be a robust, effective and versatile workhorse. Exported widely, the Mil Mi-8 remains in service with many armed forces.
Developed by Belsimtek with help from a seasoned Mi-8 pilot, the DCS: Mi-8MTV2 ‘Magnificent Eight’ was created by the same expert team behind the DCS: UH-1H Huey. Take the controls and enjoy the space where virtual meets reality.

The helicopter is equipped with lateral, longitudinal, integrated collective pitch-throttle, and directional flight control subsystems. Control inputs are transferred from the cockpit to the rotor blades by mechanical linkages and hydraulic servos. Pilot control is assisted by an automatic flight control system (AFCS) with an integrated four channel autopilot, the hydraulic flight control servos, and pitch, roll, and yaw trim systems. Both the pilot and copilot have collective, cyclic, and directional controls, which are carried by mechanical linkage to the first and second stage control units which combine, sum, and couple the cyclic, collective, and yaw inputs. Resultant output signals are boosted and routed to the main and tail rotors through mechanical linkages with the hydraulic servos.
Lateral and longitudinal control of the helicopter is by movement of the cyclic sticks through push rods, bell cranks, and servos to the main rotor swashplate. Movement in any direction tilts the plane of the main rotor blades in the same direction, thereby causing the helicopter to move in that direction.
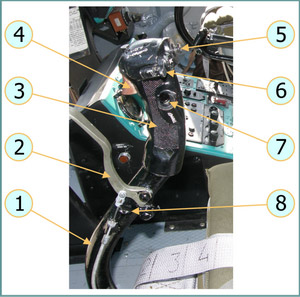
The cyclic stick is mounted on the cockpit floor in front of the pilot's seat. The stick assembly is of metal construction and includes a wheel brake lever and lock. The grip includes a three position ICS/RADIO button, an AUTOPILOT DISENGAGE button, a weapons FIRE button, and a TRIM control button. The FIRE button has a guard to prevent accidental activation.
A hydraulic cylinder and mechanical stop are included in the longitudinal control linkage to limit swashplate aft tilt to a maximum of 2°12' when the helicopter is on the ground or taxiing. The stop is controlled by weight-on-wheels microswitches mounted on the main landing gear strut supports. As the pilot pulls back on the cyclic, the longitudinal stop causes a sharp increase in the force required to move the stick when the swash plate aft tilt reaches 2°12'. As the helicopter lifts off the ground, the microswitch contacts open and the stop disengages, releasing the limit on aft swashplate tilt.








